
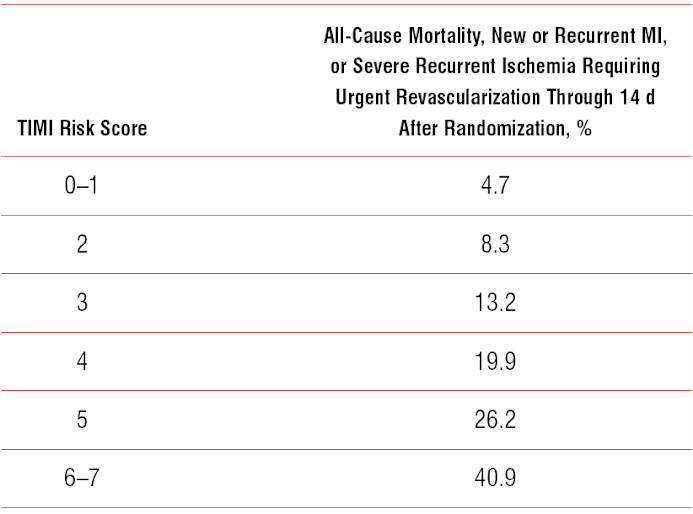
In addition, we reviewed the reference list from all identified articles to identify other papers by using graded response scales for cerebral perfusion, whether or not these papers referenced or utilized the original TICI paper. We searched for the terms “TICI” and “thrombolysis in cerebral infarction.” We also used these databases to search for all articles from January 2004 through May 2012 that cited the original TICI paper. We performed a search of the medical literature by using the ISI Web of Knowledge and SciVerse Scopus databases. Although the TICI scale has achieved fairly rapid acceptance into the medical literature, the scale was somewhat arbitrarily created and has not been validated or tested systematically. The “partial perfusion” category (grade 2) is defined as cases in which contrast passes the obstruction but with rates of entry and washout slower than normal and is subdivided into 2 subcategories, 2a and 2b. As originally described, TICI categories span from no perfusion (grade 0) to complete perfusion (grade 3). This new scale, the Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction scale, was intended to standardize the grading of angiographic outcomes, particularly for trials of endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke ( Table 1). 1 In 2003, Higashida et al 2 proposed a seemingly simple modification of the TIMI scale to evaluate intracranial perfusion assessed in cerebral angiography. The Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction scale is a widely applied, graded response scale for assessment of treatment outcome in the coronary arteries. Furthermore, patients presenting to ED with chest pain, the optimal strategy for a 2% to 4% miss rate threshold probability should be to discharge these patients from the ED.ABBREVIATIONS: TICI Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction TIMI Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction DCA showed net benefit of using HEART score is equally predictive of 6-week MACE when compared to TIMI.In non-high CV risk AA patients, HEART score is better predictive tool for 6-week MACE when compared to TIMI score. 011) using TIMI score with increase in risk category from low to high and c-statistic of 0.86 vs. 004) with increase in risk category from low to moderate vs. The univariate logistic regression model shows odds ratio of predicting 6-week MACE using HEART score was 3.11 (95% confidence interval 1.43-6.76, P =. Six hundred sixty-three patients had low TIMI score vs. 317 patients who had moderate HEART score. Decision curve analysis (DCA) was constructed to differentiate between clinical strategies in non-high CV risk patients.Of the 817 patients included, 500 patients had low HEART score vs. Logistic regression model was computed to predict 6-week and 1-year MACE and 90-day cardiac readmission. We utilized history, electrocardiogram, age, risk factors, and initial troponin (HEART) and thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) scores to predict major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in non-high cardiovascular (CV) risk predominantly AA patient population.A retrospective emergency department (ED) charts review of 1266 chest pain patients where HEART and TIMI scores were calculated for each patient. Validated risk scoring systems in African American (AA) population are under studied.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
